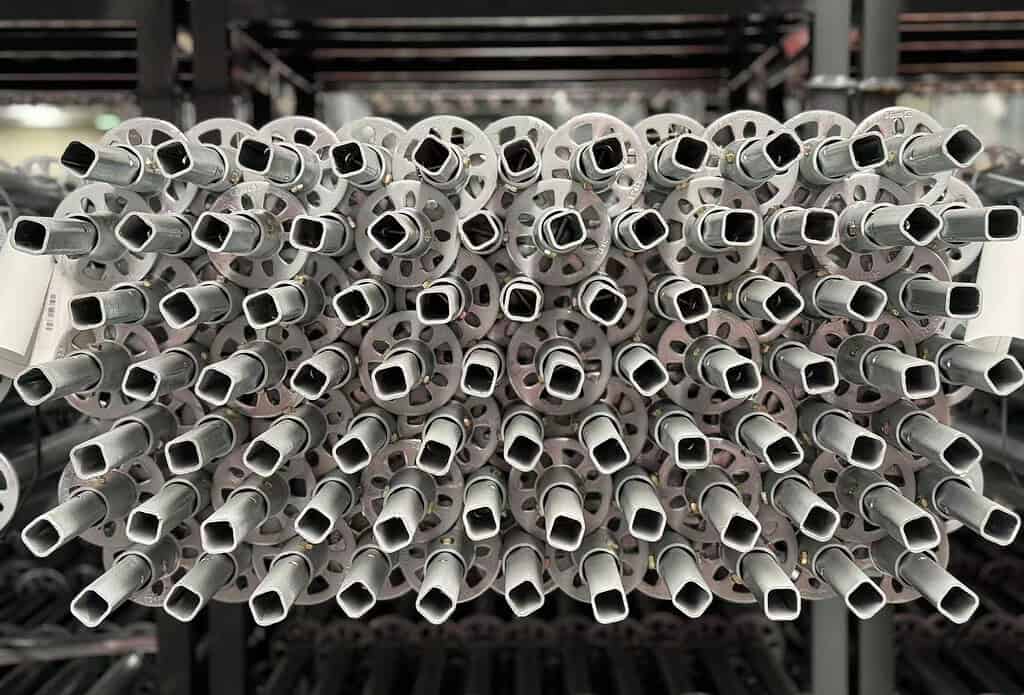
En la construcción moderna, los andamios son más que un simple sistema de soporte: son la columna vertebral de la seguridad y la eficiencia en la obra. Y cuando se trata de andamios, la elección de los materiales puede ser la diferencia entre una estructura sólida y segura y una menos confiable. Entre los diferentes sistemas de andamios disponibles, Andamios Ringlock destaca por su excepcional capacidad de carga, características de seguridad y rápido montaje. En el corazón de este sistema se encuentra el vertical (también se llama estándar), y el material más comúnmente utilizado para ello es Acero Q355Pero, ¿qué hace que el acero Q355 sea la opción ideal para los postes verticales? En este blog, analizaremos en profundidad las razones por las que el acero Q355 es el material ideal para los andamios.

¿Qué es el acero Q355?
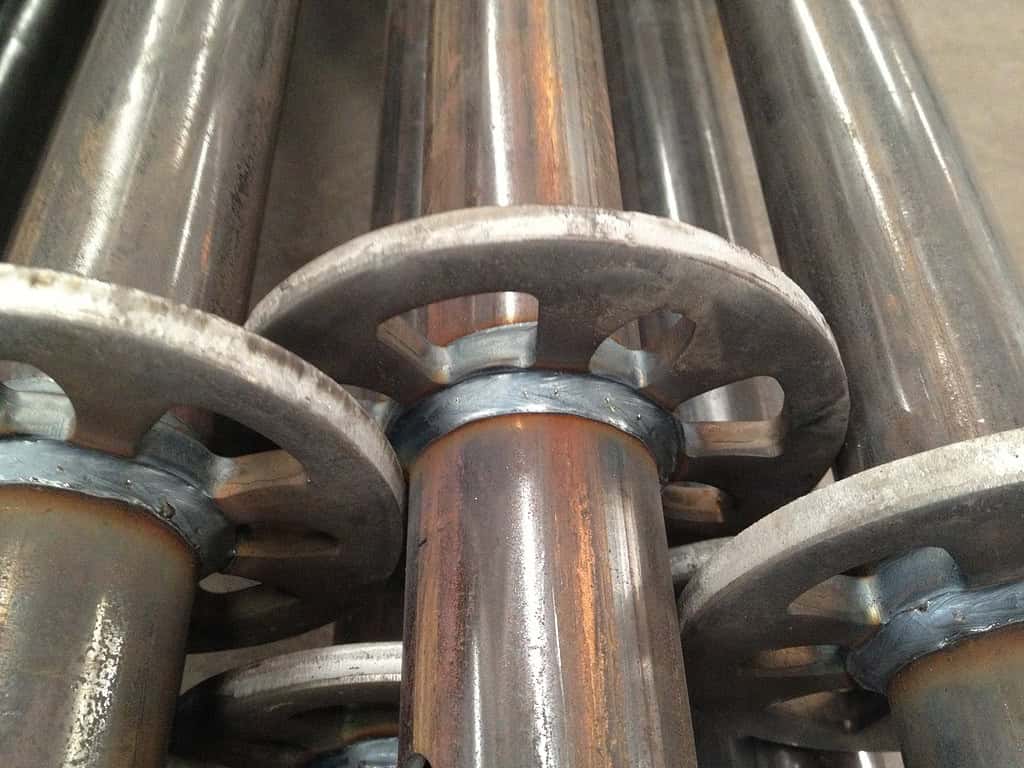
El Q355 es un tipo de acero estructural de baja aleación y alta resistencia. La “Q” representa su límite elástico, que es 355 MPa (megapascales)Esta alta resistencia al límite elástico hace que el Q355 sea perfecto para aplicaciones donde capacidad de carga y durabilidad son fundamentales. De hecho, la mayoría de las normas mundiales sobre andamios, especialmente en los principales mercados de la construcción, exigen que los postes verticales estén fabricados con materiales que cumplan o superen la resistencia de Q345/Q355.
¿Por qué no utilizar Q355 para todas las piezas del andamio?

Mientras Acero Q355 es la mejor opción para postes verticales y otros componentes, como horizontal (libro mayor) y soporte diagonal, generalmente están hechos de materiales como Q235 o Pregunta 195¿Por qué? Porque las distintas partes del sistema de andamiaje se enfrentan a distintos tipos de estrés:
- Andamio Vertical (andamio estándar): Estos soportan la carga principal, ya que llevan el peso directamente hacia abajo. Por eso necesitan la resistencia superior del Q355 para garantizar la estabilidad bajo cargas pesadas.
- Tirante horizontal y diagonal: Estas piezas proporcionan principalmente soporte lateral y no soportan la misma tensión vertical. Los materiales como el Q235, que tienen una resistencia moderada, son más que suficientes para estas funciones.
Los beneficios de utilizar Q355 para andamios verticales
1. Alta capacidad de carga
La alta resistencia al límite elástico del Q355 garantiza que los andamios verticales puedan soportar cargas significativas sin fallar. En las pruebas, los postes Q355 han demostrado Capacidad de carga muy superior en comparación con los materiales de andamios tradicionales. Por ejemplo, un andamio vertical estándar Q355 puede soportar hasta 99,1 kN, mientras que una versión de servicio pesado puede soportar hasta 136,5 kN.
2. Durabilidad y resistencia al impacto
El acero Q355 es increíblemente duradero y tiene una excelente resistencia a los impactos, incluso en condiciones adversas como el clima frío. Su dureza minimiza el riesgo de fracturas frágiles, lo que lo hace más seguro y confiable para un uso a largo plazo. Esto es especialmente importante en entornos de construcción donde el andamio está expuesto al desgaste.
3. Versatilidad y flexibilidad
El uso de acero Q355 no solo significa un andamio vertical más resistente, sino que también permite diseños de andamios más flexibles. Los contratistas pueden usar menos materiales para lograr tramos de andamios más amplios, lo que les da a los trabajadores más espacio interno para operar. Esta flexibilidad puede ayudar a reducir los costos de material y acelerar los plazos del proyecto, ofreciendo tanto ventajas económicas y prácticas.
La importancia del control de calidad en los andamios verticales Q355
Sin embargo, no basta con utilizar acero Q355. La forma en que se procesa el acero, en particular cuando se convierte en tuberías, puede afectar su rendimiento. Las investigaciones muestran que tanto la elongación como la tenacidad pueden disminuir durante el proceso de fabricación. Además, la calidad de las soldaduras, especialmente en las juntas, es crucial para garantizar la resistencia y la estabilidad generales del andamio. Por eso Control de calidad riguroso Es esencial garantizar que el producto terminado cumpla con los estándares de seguridad.
Comprensión de la capacidad de carga de los andamios verticales tipo B y tipo Z en andamios Ringlock
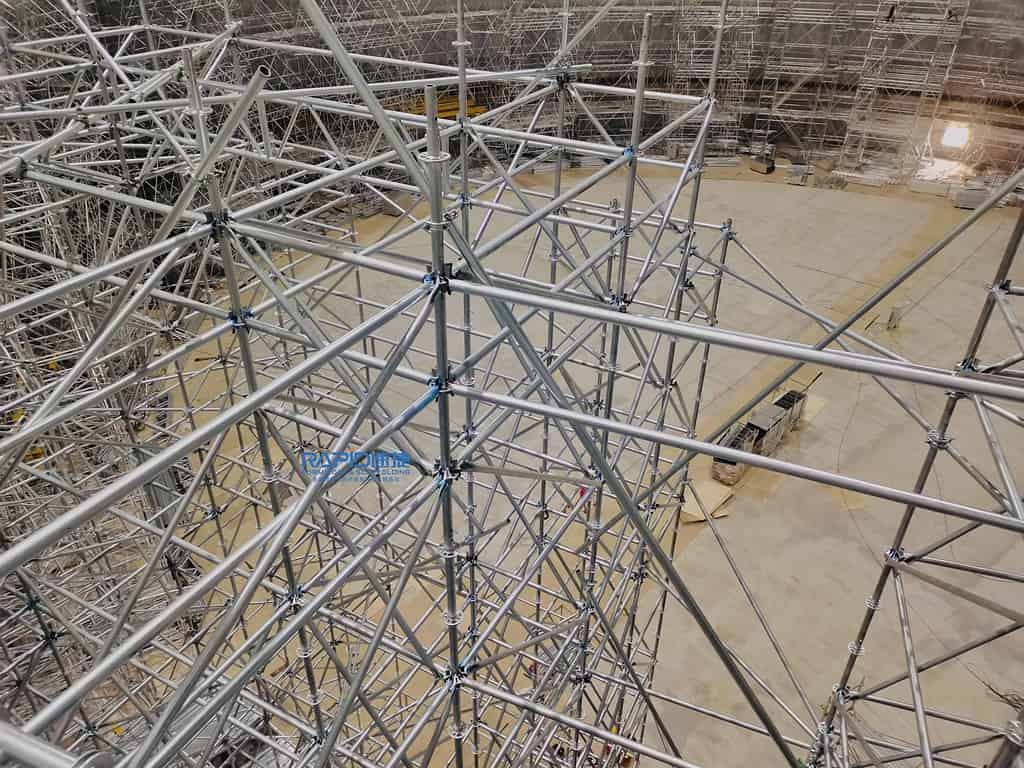
Los andamios Ringlock son conocidos por su capacidad de carga superior y su diseño robusto, lo que los convierte en la opción preferida para muchos proyectos de construcción. Exploramos Tipo B (tradicional) y Tipo Z (servicio pesado) Los andamios verticales están fabricados en acero Q355 de alta resistencia y presentan capacidades de carga calculadas y probadas.
Verticales tipo B y tipo Z: diferencias clave
| Tipo | Diámetro exterior (mm) | Espesor de la pared (mm) | Área seccional (mm²) | Momento de inercia (mm⁴) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tipo B | 48.3 | 3.2 | 453 | 16.0 |
| Tipo Z | 60.3 | 3.2 | 574 | 20.2 |
La principal diferencia entre ambos tipos radica en su diámetro y capacidad de carga, lo que afecta su rendimiento en los sistemas de andamios.
Capacidad máxima de carga calculada
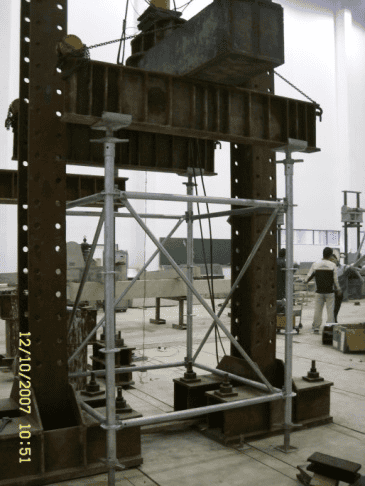
Utilizando las fórmulas especificadas por las normas técnicas de seguridad, las capacidades máximas admisibles de carga de diseño para los verticales son las siguientes:
| Tipo | Coeficiente de estabilidad (φ) | Carga máxima (kN) |
|---|---|---|
| Tipo B (48,3 mm) | 0.350 | 47.6 |
| Tipo Z (60,3 mm) | 0.516 | 88.9 |
Estos valores se derivan del coeficiente de estabilidad (φ) del acero Q355 y de las características específicas de cada tipo vertical.
Resultados de la prueba experimental de capacidad de carga
Para verificar las capacidades calculadas, se realizaron pruebas de carga en el mundo real con la siguiente configuración:
- Espaciado vertical: 1500 mm (longitudinal y transversal)
- Altura del escalón: 1500 milímetros
- Refuerzo diagonal completo
Los resultados de estas pruebas muestran el rendimiento de carga real de los verticales.
| Tipo | Carga máxima para 4 postes (kN) | Carga máxima por polo (kN) |
|---|---|---|
| Tipo B | 396.3 | 99.1 |
| Tipo Z | 546.0 | 136.5 |
Estos resultados de pruebas demuestran claramente que La capacidad de carga de un solo poste vertical de andamio en el sistema Ringlock supera con creces la de los postes de andamio tradicionales.Esta mayor capacidad de carga permite una mayor amplitud del andamio, lo que aumenta el espacio de trabajo interno y proporciona una mayor flexibilidad para las operaciones en la obra. Además, esta ventaja ayuda a reducir el consumo de material y acorta los plazos del proyecto, lo que en última instancia se traduce en beneficios económicos directos para los clientes.
Las pruebas de carga exhaustivas resaltan la resistencia y confiabilidad de los andamios Ringlock, especialmente cuando se utiliza acero Q355 para postes verticales de andamios. Ya sea que trabaje en edificios de gran altura, puentes o proyectos industriales a gran escala, el rendimiento superior de los postes verticales de tipo B y tipo Z ofrece una clara ventaja en términos de seguridad y eficiencia.
Puntos clave
- Capacidad de carga superior: Los postes verticales de andamios tipo B (99,1 kN) y tipo Z (136,5 kN) superan significativamente a los sistemas de andamios tradicionales, ofreciendo mayor estabilidad y seguridad.
- Ganancias de eficiencia: La mayor capacidad de carga permite utilizar menos materiales y tramos de andamios más amplios, lo que reduce costos y acorta los plazos de construcción.
- Garantía de seguridad: El uso de acero Q355 y pruebas rigurosas garantiza que los postes tipo B y tipo Z sean altamente confiables y puedan satisfacer de manera segura las demandas de proyectos a gran escala.
Conclusión
En resumen, el acero Q355 se destaca como el material ideal para postes verticales en andamios Ringlock, gracias a su excepcional capacidad de carga, resistencia al impacto y durabilidad. Su resistencia para soportar cargas pesadas y soportar duras condiciones ambientales garantiza tanto la seguridad como la eficiencia en las obras de construcción. Ya sea que opten por verticales de tipo B o de tipo Z, los contratistas se benefician de un menor uso de material, un montaje más rápido y plazos de proyecto mejorados. Al elegir acero Q355 para su sistema de andamios, está invirtiendo en confiabilidad a largo plazo, mayor seguridad y ahorros de costos significativos.
Si desea obtener más información sobre materiales para andamios o necesita materiales de alta calidad Andamio RinglockNo dudes en ponerte en contacto con nosotros. ¡Estaremos encantados de ayudarte!
